MSIX doesn’t natively support shortcut arguments. This blog explains how we can use the Package Support Framework (PSF) to add MSIX shortcut arguments/parameters.
Install the Package Support Framework (PSF)
There are two options to install the PSF for MSIX.
Option 1 – Manually Download PSF for MSIX
- Navigate to the Package Support Framework page on Nuget: https://www.nuget.org/packages/Microsoft.PackageSupportFramework/
- Click Download Package and you will download a file called something similar to: microsoft.packagesupportframework.[version].nupkg
- Rename the extension from nupkg to zip, and extract it.
- Navigate to the bin folder and copy all the contents somewhere local. These files form the Package Support Framework and we’ll need some of them later on.
Option 2 – Install PSF for MSIX using Powershell
Follow our post on how to install the Package Support Framework for MSIX using PowerShell.
Add Shortcut Arguments/Parameters To Your MSIX
-
-
- Open your MSIX in edit mode using the MSIX Packaging Tool.
- Navigate to the Package Information tab and scroll down to the Manifest File section. Click Open File, and it will open the AppxManifest.xml file for your package.
- In the AppxManifest.xml file will be a node called
Applications, and this may contain one or many sub-nodes calledApplication. This represents all the applications in your package and will look similar to this:<Applications> <Application Id="ALKANEAPP" Executable="VFS\ProgramFilesX86\Alkane\Alkane.exe" EntryPoint="Windows.FullTrustApplication"> <uap:VisualElements BackgroundColor="transparent" DisplayName="Alkane Solutions" Square150x150Logo="Assets\ALKANEAPP-Square150x150Logo.png" Square44x44Logo="Assets\ALKANEAPP-Square44x44Logo.png" Description="Alkane Solutions"> <uap:DefaultTile Wide310x150Logo="Assets\ALKANEAPP-Wide310x150Logo.png" Square310x310Logo="Assets\ALKANEAPP-Square310x310Logo.png" Square71x71Logo="Assets\ALKANEAPP-Square71x71Logo.png" /> </uap:VisualElements> <Extensions> <desktop7:Extension Category="windows.shortcut"> <desktop7:Shortcut File="[{Programs}]\Alkane\Alkane Solutions.lnk" Icon="VFS\ProgramFilesX86\Alkane\App.exe" /> </desktop7:Extension> </Extensions> </Application> </Applications> - Make a note of the Application Id
ALKANEAPPand also the Executable value ofVFS\ProgramFilesX86\Alkane\Alkane.exebecause we’ll need these values later. - Change the Executable value to be
PsfLauncher32.exe. We are now telling the package that when the shortcut is clicked we want to launchPsfLauncher32.exeand NOTAlkane.exe. The second line should now look like this:<Application Id="ALKANEAPP" Executable="PsfLauncher32.exe" EntryPoint="Windows.FullTrustApplication"> - Now save the file and close it.
- We now need to add the PSF files to our package. Navigate to the Package Files tab, right click on the Package folder and click Add file….
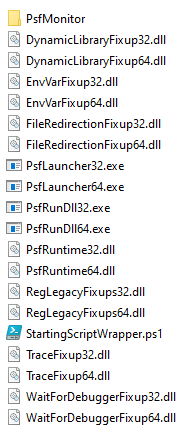
- From your downloaded Package Support Framework (PSF) select the following 6 files (hold down ctrl to select them all) and add them to your package (we don’t need the others, which are related to PSF ‘fixups’):
- PsfLauncher32.exe
- PsfRuntime32.dll
- PsfRunDll32.exe
- PsfLauncher64.exe
- PsfRuntime64.dll
- PsfRunDll64.exe
Note – we really only need to add the files for our application architecture (NOT our operating system architecture). So if our application was 32-bit and our operating system was 64-bit, we would just add the 3 files containing ’32’.
- Now we know our package is opening PsfLauncher32.exe, but it doesn’t know what to do with it! So we need to create a file called config.json to tell our package what to do.
- Open notepad (or Notepad++) and create/save a file called
config.jsonwith the following content:{ "applications": [ { "id": "ALKANEAPP", "executable": "VFS\\ProgramFilesX86\\Alkane\\Alkane.exe", "arguments": "-alkaneargument" }] } - You will notice that we have referenced the application ID in the AppxManifest.xml (ALKANEAPP), and we have specified the executable to be the original executable in the AppxManifest.xml (VFS\\ProgramFilesX86\\Alkane\\Alkane.exe). You will also notice that for valid JSON we either need to escape backslashes with another backslash (\\) or we need to replace them with a forward slash. Finally you will notice that we are passing in an argument of
-alkaneargument. - We now need to add the config.json to our package. Navigate to the Package Files tab, right click on the Package folder and click Add file….
- Add the config.json file, which should sit alongside the PSF files you added earlier.
- Save your package and test it.
-
We have essentially told our MSIX shortcut to launch PsfLauncher32.exe from the shortcut. PsfLauncher32.exe will then read the config.json file and subsequently launch VFS\\ProgramFilesX86\\Alkane\\Alkane.exe with an argument of -alkaneargument.